this post was submitted on 15 Sep 2024
353 points (97.8% liked)
Science Memes
10309 readers
1105 users here now
Welcome to c/science_memes @ Mander.xyz!
A place for majestic STEMLORD peacocking, as well as memes about the realities of working in a lab.

Rules
- Don't throw mud. Behave like an intellectual and remember the human.
- Keep it rooted (on topic).
- No spam.
- Infographics welcome, get schooled.
Research Committee
Other Mander Communities
Science and Research
Biology and Life Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !reptiles and [email protected]
Physical Sciences
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Humanities and Social Sciences
Practical and Applied Sciences
- !exercise-and [email protected]
- [email protected]
- !self [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Memes
Miscellaneous
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
you are viewing a single comment's thread
view the rest of the comments
view the rest of the comments
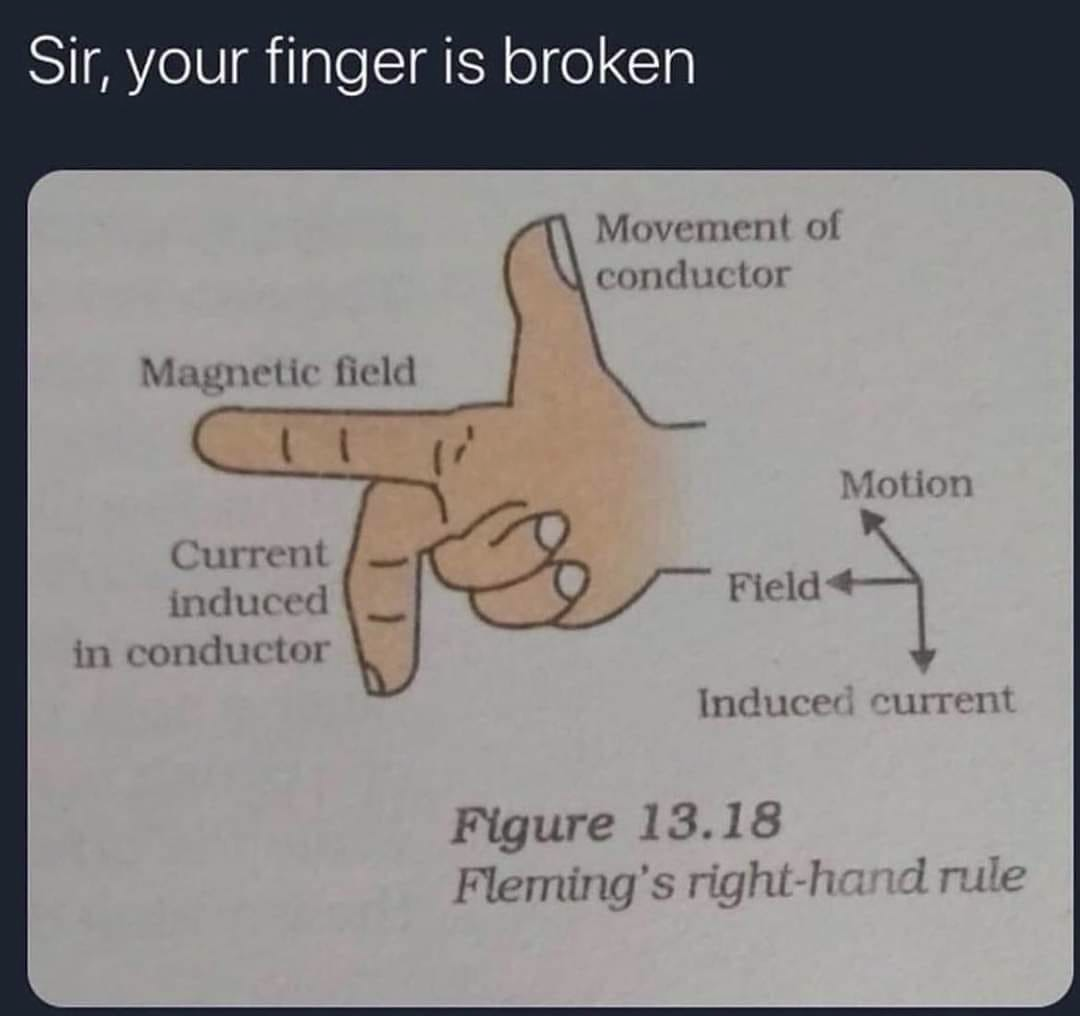
I think the confusing part is that the rule is presented without the problem it solves.
The problem is when you take two vectors in 3d and want to find the vector orthogonal (perpendicular) to both, you have 2 valid choices.
The right hand rule is a way to pick the same one every time if you always label the two vectors you start with consistently i.e. make your thumb vector 1, pointer vector 2, then your middle finger points the direction of a perpendicular vector that matches the handedness of the hand you used.
This matters anywhere a vector cross product is used in physics, like calculating what direction an electron feels force when moving through a magnetic field. The physics doesn't change, but you'll have negatives in different places when comparing results calculated with a right handed convention (coordinate system) with a left handed convention.
When checking the handedness of your coordinate system, you point your thumb and pointer finger in the positive direction of any two dimensions then check if your middle finger points in the positive direction of the third dimension.