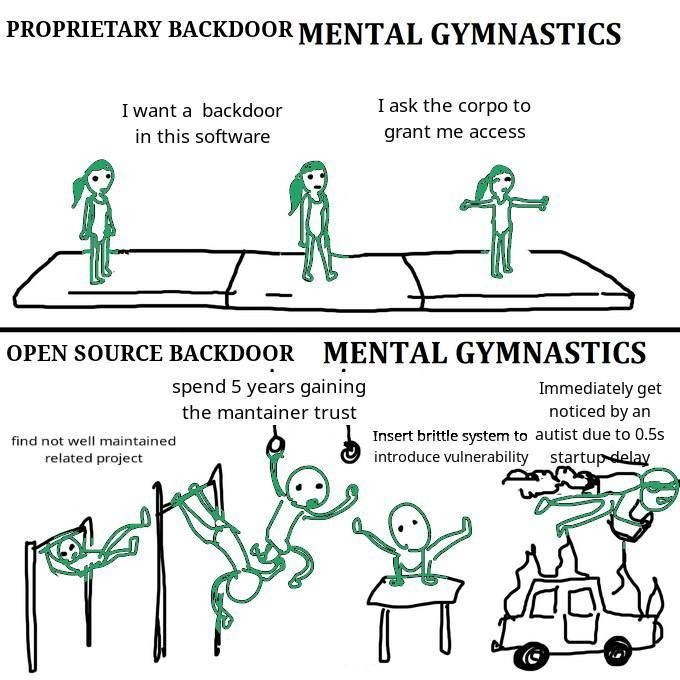
Cheeky answer:

Actual answer:
Theoretically anyway, open source software's guarantee of "no backdoor" is that the code is auditable, and you could study it and know if it has any holes and where. Of course, that presumes that you have the knowledge AND time to actually go and study thousands of lines of code. Unrealistic.
Slightly less guaranteed but still good enough to calm my mind, is the idea that there is a whole-ass community of people who do know their shit and who are constantly checking this.
Do note that like. Closed source software is known to be backdoored, only, the backdoors are mostly meant for either the owners of the software (check the fine print folks) or worse, the governments.
The biggest thing that you should note is that: It is unlikely that you (or I or most of the people here) are interesting enough that anyone will actually exploit those vulnerabilities to personally fuck you over. Your photos aren't interesting enough except as part of a mass database (which is why Google/Facebook want them). Same for your personal work data and shit.
Unless those backdoors could be used to turn your machine into a zombie for some money-making scheme (crypto or whatever) OR you're connected to people in power OR you personally piss off someone who is a hacker -- it is very unlikely you'll get screwed over due to those vulnerabilities :P